Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG): Overview
Interventional Radiology
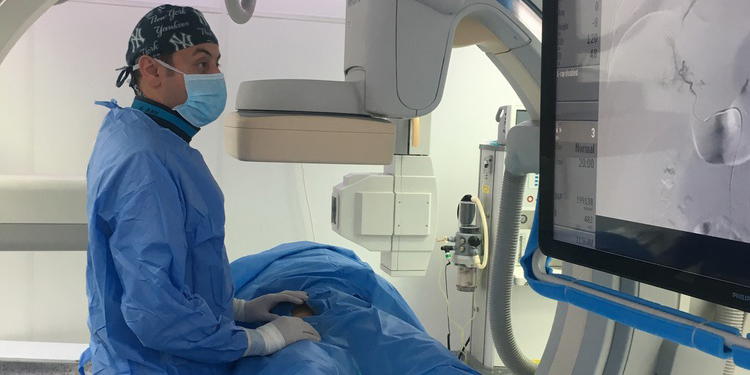
Interventional radiology (IR) is a rapidly advancing field in modern medicine that combines imaging technologies with minimally invasive procedures to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions. Often referred to as "image-guided therapy," interventional radiology uses tools like X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound to guide precision treatments that reduce recovery times, minimize risks, and often eliminate the need for traditional surgery.
In this guide, we will delve into the basics of interventional radiology, how it works, its benefits, and its diverse applications in healthcare.
A Brief History of Interventional Radiology
The roots of interventional radiology can be traced back to the mid-20th century. The specialty began to take shape with the advent of angiography—an imaging technique used to visualize blood vessels—developed in the 1920s. However, it wasn’t until the 1960s that interventional radiology became a distinct discipline. Dr. Charles Dotter, often regarded as the "father of interventional radiology," pioneered catheter-based treatments that laid the groundwork for the specialty. Over the years, advancements in imaging technology and medical devices have propelled IR into the forefront of modern medicine.
How Does Interventional Radiology Work?
Interventional radiology relies on advanced imaging technologies to perform minimally invasive procedures. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Imaging Guidance: High-resolution imaging techniques such as fluoroscopy, CT, or ultrasound are used to visualize internal structures in real time.
- Access: A small incision or puncture is made, usually under local anesthesia, to insert a thin catheter or needle into the targeted area.
- Treatment: Specialized tools are used to perform the procedure, whether it’s delivering medication, removing blockages, or deploying medical devices like stents.
- Post-Procedure Monitoring: After the procedure, imaging is used to confirm the success of the treatment and monitor recovery.
Benefits of Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology offers numerous advantages over traditional surgical methods, making it a preferred option for many patients and healthcare providers. Key benefits include:
- Minimally Invasive: Procedures are performed through small incisions, reducing the risk of complications such as infection and excessive bleeding.
- Faster Recovery: Patients typically experience less pain and shorter recovery times compared to open surgery.
- Lower Risk: IR procedures often require only local anesthesia, minimizing the risks associated with general anesthesia.
- Precision: Advanced imaging allows for targeted treatment, reducing damage to surrounding tissues.
- Outpatient Options: Many interventional procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis, eliminating the need for prolonged hospital stays.
Common Procedures in Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiologists treat a wide range of conditions across various medical specialties. Some of the most common procedures include:
- Angioplasty and Stenting: Treating blocked or narrowed blood vessels using a balloon-tipped catheter and possibly placing a stent.
- Embolization: Blocking abnormal blood vessels to treat conditions such as uterine fibroids, AVMs, or tumors.
- Biopsy and Drainage: Using imaging guidance to perform needle biopsies or drain abscesses and fluid collections.
- Cancer Treatments: Procedures such as RFA and TACE target tumors directly, sparing healthy tissues.
- Dialysis Access Management: Maintaining or restoring function in vascular access points for dialysis patients.
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Treating spinal fractures with injected cement-like material to stabilize and reduce pain.
Who Performs Interventional Radiology?
Interventional radiology is performed by specialized physicians known as interventional radiologists. These doctors undergo extensive training, which includes:
- Completing medical school.
- Completing a residency in diagnostic radiology.
- Pursuing fellowship training in interventional radiology.
Interventional radiologists collaborate with other medical specialists, such as oncologists, cardiologists, and surgeons, to provide comprehensive patient care.
Applications of Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology has applications in nearly every area of medicine, including:
- Cardiology: Treating blocked arteries, heart valve issues, and congenital abnormalities.
- Oncology: Minimally invasive cancer treatments and pain management.
- Gastroenterology: Managing gastrointestinal bleeding, biliary obstructions, and liver disease.
- Gynecology: Treating uterine fibroids and pelvic pain syndromes.
- Orthopedics: Addressing bone and joint issues, such as fractures and arthritis-related pain.
- Nephrology: Assisting in kidney-related procedures, including placement of nephrostomy tubes.
What to Expect During an IR Procedure
If you or a loved one are scheduled for an interventional radiology procedure, here is a general overview of what to expect:
- Pre-Procedure: Imaging and consultation to determine the best approach. Fasting may be required for certain procedures.
- During the Procedure: Local anesthesia will be administered, and you may remain awake but sedated. Imaging will guide the treatment.
- Post-Procedure: Recovery is often quick, with minimal pain. Follow-up imaging may be scheduled to monitor progress.
The Future of Interventional Radiology
The field of interventional radiology continues to evolve with advancements in technology and techniques. Innovations such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and improved imaging modalities are expanding the possibilities for even less invasive and more precise treatments. As the healthcare landscape shifts toward personalized medicine, interventional radiology is poised to play an increasingly central role.
Conclusion
Interventional radiology is a groundbreaking medical specialty that bridges the gap between diagnostic imaging and therapeutic intervention. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and minimally invasive techniques, it offers safer, faster, and more effective treatment options for a myriad of conditions. Whether you’re a patient seeking alternatives to traditional surgery or a healthcare professional exploring advanced treatment options, interventional radiology represents the future of medicine—a future where precision and compassion go hand in hand.

